3258. Fibonacci sequence
The Fibonacci
sequence is defined as follows:
a0 = 0
a1 = 1
ak = ak-1 + ak-2
For a given value
of n, find the n-th element of the Fibonacci sequence.
Input. One positive
integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 40).
Output. Print the n-th element of the Fibonacci sequence.
|
Sample
input 1 |
Sample
output 1 |
|
2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
Sample
input 2 |
Sample
output 2 |
|
5 |
5 |
SOLUTION
Fibonacci numbers
Algorithm
analysis
In this problem you must
find the n-th Fibonacci number. For n ≤ 40, a recursive implementation will pass time limit. The Fibonacci sequence has
the following form:
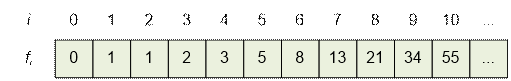
The largest Fibonacci number that fits into
the int type is
f46 = 1836311903
For n ≤ 40 it’s sufficient to use the int data type.
Let
the function fib(n) compute the n-th Fibonacci number. Then we have the following recurrence
relation:
fib(n)
= 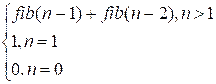
Algorithm implementation
The fib function computes the n-th Fibonacci number.
int fib(int n)
{
if (n == 0) return 0;
if (n == 1) return 1;
return fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2);
}
The main part of the program. Read the value of n,
compute and print the value of fib(n).
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("%d\n", fib(n));
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static int f(int n)
{
if (n == 0) return 0;
if (n == 1) return 1;
return f(n-1) + f(n - 2);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
System.out.println(f(n));
con.close();
}
}
Python implementation – memoization
The fib function computes the n-th Fibonacci number.
def fib(n):
if dp[n] != -1:
return dp[n]
dp[n]
= fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2)
return dp[n]
The main part of the program. Read the input value of n.
n = int(input())
Initialize
the list dp.
dp = (n + 1) * [-1]
dp[0] = 0
dp[1] = 1
Compute
and print the answer.
print(fib(n))
Python implementation – memoization 2
arr = {}
The fib function computes the n-th Fibonacci number.
def fib(n):
if (n ==
0): return 0
if (n ==
1): return 1
if n not in
arr:
arr[n] = fib(n - 1) +
fib(n - 2)
return
arr[n]
The main part of the program. Read the value of n,
compute and print the value of fib(n).
n = int(input())
print(fib(n))
Python implementation – memoization 3
arr = {0:0, 1:1}
The fib function computes the n-th Fibonacci number.
def fib(n):
if arr.get(n)
is None:
arr[n] = fib(n - 1) +
fib(n - 2)
return
arr[n]
The main part of the program. Read the value of n,
compute and print the value of fib(n).
n = int(input())
print(fib(n))
Python implementation – TLE
The fib function computes the n-th Fibonacci number.
def fib(n):
if (n ==
0): return 0
if (n ==
1): return 1
return
fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2)
The main part of the program. Read the value of n,
compute and print the value of fib(n).
n = int(input())
print(fib(n))